
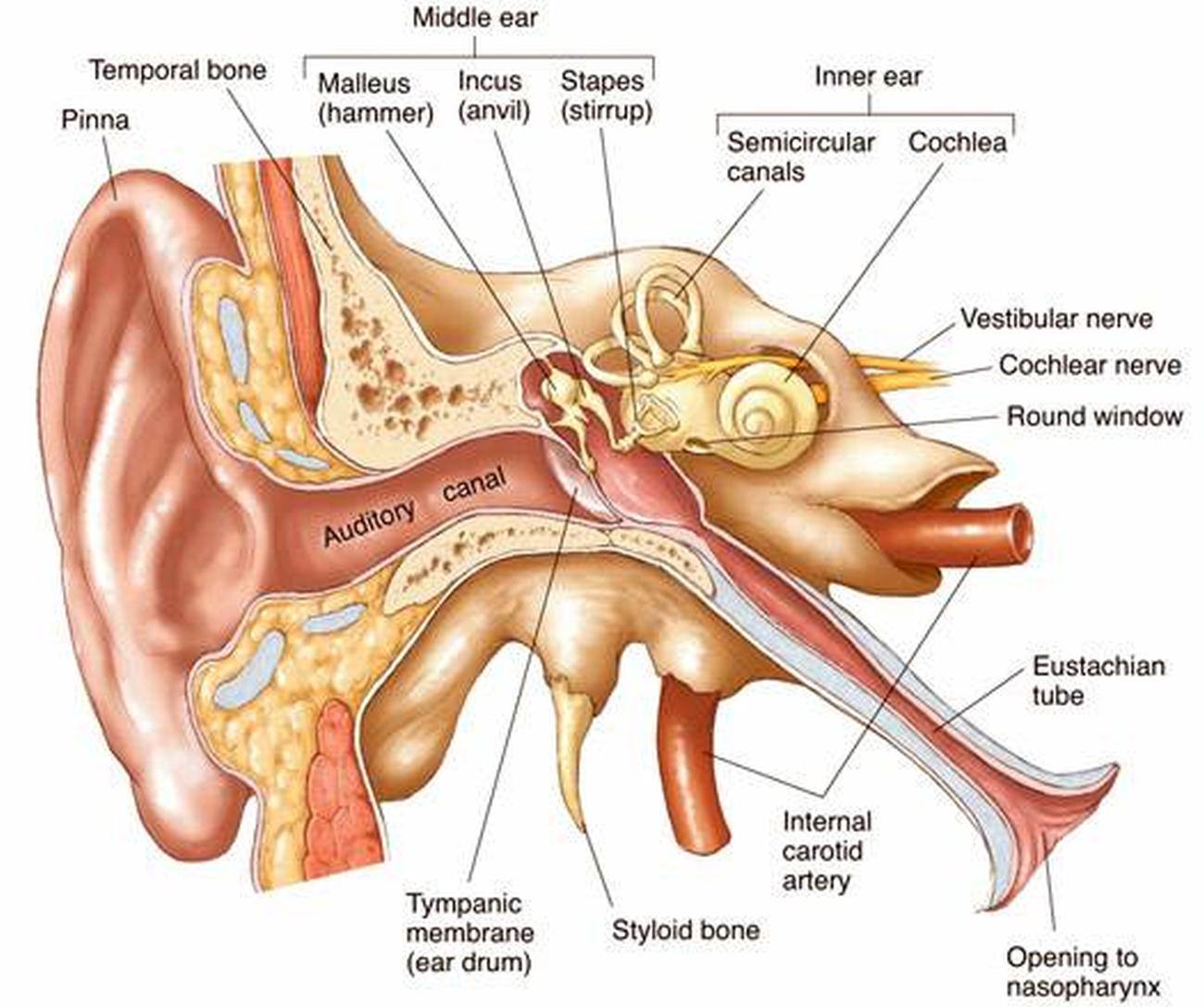

The lateral walls of the nasopharynx are made of the pharyngeal ostia (bone) of the auditory tube, and supported by the torus tubarus, a mound of cartilage tissue from the auditory tube. While loss of the adenoids does not make a significant difference in immune system function, the procedure occasionally has complications. The adenoids are often removed in childhood due to infection or hypertrophy (enlargement of the cells in its tissues), which can obstruct the flow of air from the nose to the lung if left untreated. The adenoids play a minor role in embyonic development and have a minor role in producing T-lymphocytes for the immune system after birth. The adenoids (pharyngeal tonsils) are a mass of lymphatic tissue found in the roof of the nasopharynx. The nasopharynx contains psuedo-stratified squamous cell epithelia tissue that is ciliated (covered in tiny hairs that move mucus). However, it also allows infections to spread easily between the nasopharynx and ear. The nasopharynx connects to the eustachian tubes of the middle ear, which allows the nasopharynx to help balance pressure within the ear. The nasophaynx connects the nasal cavity with the throat. It extends from the base of the skull to the upper surface of the soft palate above the oral cavity. The nasopharynx is the upper region of the pharynx. The Pharynx: This is a detailed diagram of the pharynx from Gray’s Anatomy, showing the major structures in each part of the pharynx. The laryngopharynx is the bottom part of the pharynx that marks the branching pathway between the digestive and respiratory systems.The oropharynx is the middle chamber of the pharynx that passes food from the mouth into the laryngopharynx.Two of the major sets of tonsils are the adenoids in the nasopharynx, and the palatine tonsils in the oropharyx. Tonsils (lymphoid tissue) exist in the pharynx.The laryngopharynx includes three major sites: the pyriform sinus, postcricoid area, and the posterior pharyngeal wall.Because both food and air pass through the pharynx, a flap of connective tissue called the epiglottis closes over the glottis when food is swallowed to prevent food from getting into the lungs.The Eustachian tubes connect the middle ear to the nasopharynx, and serve to equalize the barometric pressure in the middle ear with that of the ambient atmosphere.The human pharynx is conventionally divided into three sections: the nasopharynx (epipharynx), the oropharynx (mesopharynx), and the laryngopharynx (hypopharynx).It is situated immediately posterior to (behind) the mouth and nasal cavity, and superior to (above) the esophagus and larynx. The human pharynx (plural: pharynges) is part of the digestive system and also the respiratory system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
